The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that spans 56.3 million years from the end of theTriassic Period201.3 million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period 145 Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of theMesozoic Era, also known as the Age of Reptiles. The start of the period is marked by the major TriassicJurassic extinction event. Two other extinction events occurred during the period: the Pliensbachian/Toarcian event in the Early Jurassic, and the Tithonian event at the end; however, neither event ranks among the Big Five mass extinctions.
The Jurassic is named after the Jura Mountains within the European Alps, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. By the beginning of the Jurassic, thesupercontinent Pangaea had begun rifting into two landmasses, Laurasia to the north andGondwanato the south. This created more coastlines and shifted the continental climate from dry to humid, and many of the arid deserts of the Triassic were replaced by lush rainforests.

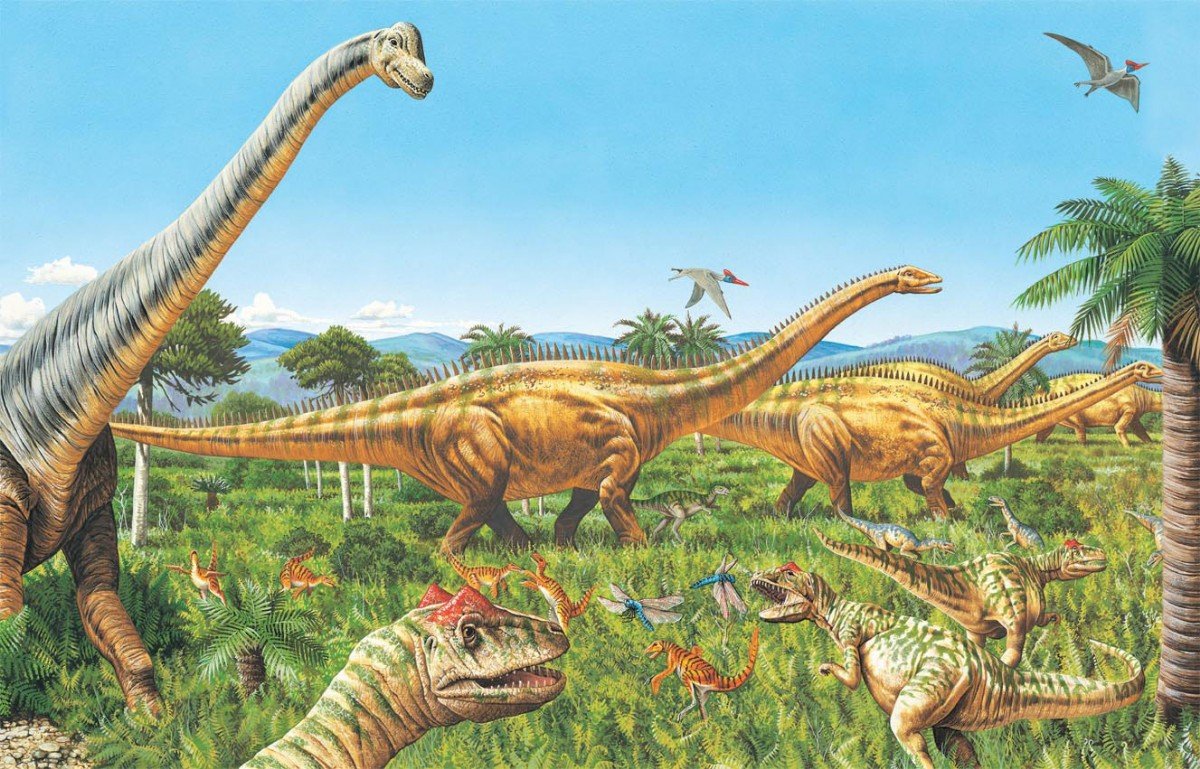
On land, the fauna transitioned from the Triassic fauna, dominated by both dinosauromorph and crocodylomorph archosaurs, to one dominated by dinosaurs alone. The firstbirdsalso appeared during the Jurassic, having evolved from a branch of theropod dinosaurs. Other major events include the appearance of the earliest lizards, and the evolution of therian mammals, including primitive placentals. Crocodilians made the transition from a terrestrial to an aquatic mode of life. The oceans were inhabited by marine reptiles such asichthyosaursandplesiosaurs, whilepterosaurs were the dominant flying vertebrates.

The Jurassic period is divided into theEarly,Middle, andLate epochs. The Jurassic System, inhistoriography, is divided into theLower,Middle, andUpper seriesof rock formations, also known as Lias , Dogger and Malm inEurope. The separation of the term into three sections goes back toLeopold von Buch. Thefaunal stagesfrom youngest to oldest are:
| Upper/Late Jurassic | |
| Tithonian | (152.1 4 145 4Mya) |
| Kimmeridgian | (157.3 4 152.1 4 Mya) |
| Oxfordian | (163.5 4 157.3 4 Mya) |
| Middle Jurassic | |
| Callovian | (166.1 4 163.5 4 Mya) |
| Bathonian | (168.3 3.5 166.1 4 Mya) |
| Bajocian | (170.3 3 168.3 3.5 Mya) |
| Aalenian | (174.1 2 170.3 3 Mya) |
| Lower/Early Jurassic | |
| Toarcian | (182.7 1.5 174.1 2 Mya) |
| Pliensbachian | (190.8 1.5 182.7 1.5 Mya) |
| Sinemurian | (199.3 1 190.8 1.5 Mya) |
| Hettangian | (201.3 0.6 199.3 1 Mya) |
During the early Jurassic period, the supercontinent Pangaea broke up into the northern supercontinent Laurasia and the southern supercontinent Gondwana; the Gulf of Mexico opened in the new rift between North America and what is now Mexicos Yucatn Peninsula. The Jurassic North Atlantic Ocean was relatively narrow, while the South Atlantic did not open until the following Cretaceous period, when Gondwana itself rifted apart. The Tethys Sea closed, and the Neotethys basin appeared. Climates were warm, with no evidence of a glacier having appeared. As in the Triassic, there was apparently no land over either pole, and no extensive ice caps existed.
The Jurassic was a time of calcite sea geochemistry in which low-magnesium calcite was the primary inorganic marine precipitate of calcium carbonate. Carbonate hardgrounds were thus very common, along with calcitic ooids, calcitic cements, and invertebrate faunas with dominantly calcitic skeletons.
The first of several massive batholiths were emplaced in the northern American cordillera beginning in the mid-Jurassic, marking the Nevadan orogeny. Important Jurassic exposures are also found in Russia, India, South America, Japan, Australasia and the United Kingdom.
In Africa, Early Jurassic strata are distributed in a similar fashion to Late Triassic beds, with more common outcrops in the south and less common fossil beds which are predominated by tracks to the north. As the Jurassic proceeded, larger and more iconic groups of dinosaurs like sauropods and ornithopods proliferated in Africa.
Also read: Pangea and Cretaceous Period